Ajoy Raman
EDN
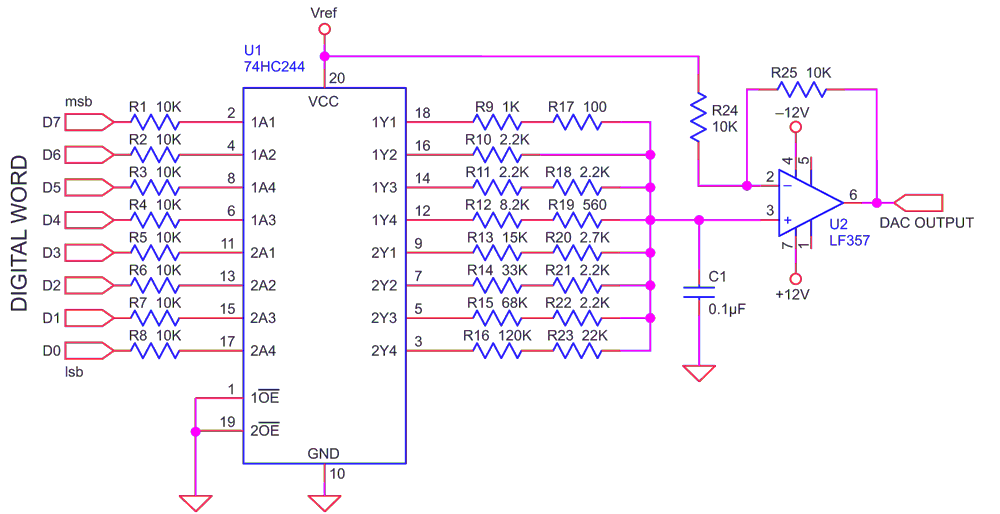
Utilizing the large operating voltage range of an octal CMOS buffer, this Design Idea presents a simple 8-bit two-quadrant multiplying Digital-to-Analog-Converter (DAC) built with the buffer/line-driver IC 74HC244.
 |
|
| Figure 1. | |
In Figure 1, an 8-bit digital word is fed through resistors R1-R8 to the eight inputs of the CMOS buffer U1. The outputs of U1 are combined through a 1:2:4:8...128 weighted resistor network formed by resistors R9-R23. The DAC reference voltage Vref is fed to U1 VCC. The outputs of U1 thus track Vref. Resistors R1-R8 are required to prevent the output voltages of U1 from being influenced by the voltage-levels of the digital inputs.
An 8-bit voltage-output unipolar DAC with Vref=VCC is formed at pin 3 of U2. C1 optionally low-pass filters this output, which is buffered, amplified by a factor two, and offset by Vref, to provide a bipolar DAC output at pin 6 of the op-amp, an LF357.
 |
|
| Figure 2. | |
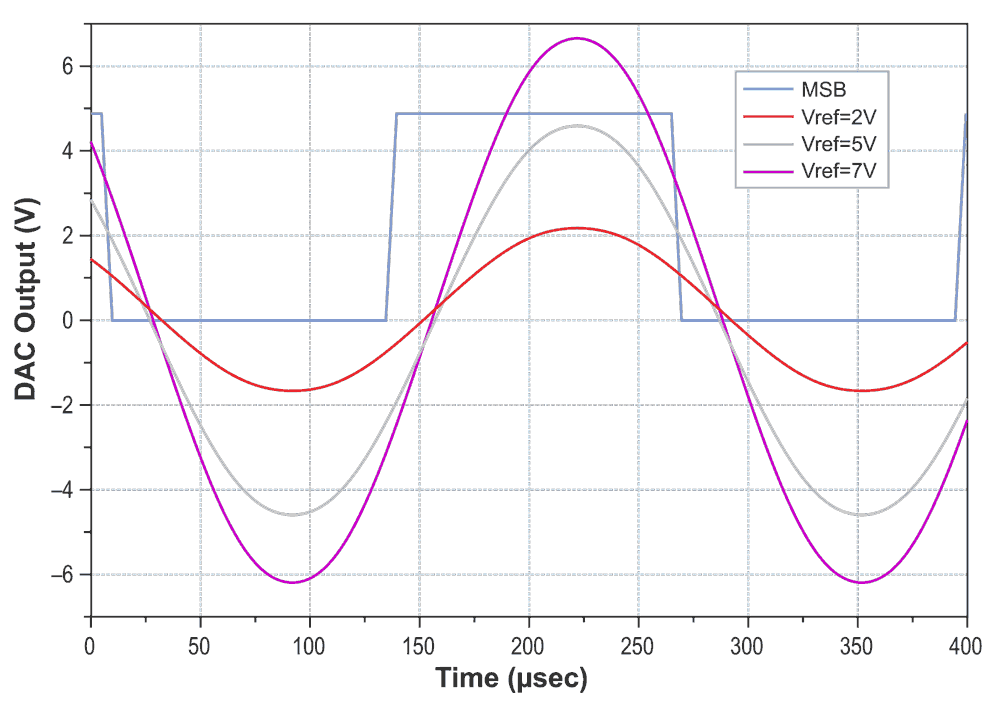
Figure 2 shows the DAC output for a 16-samples/cycle, 3750 Hz synthesized sine wave for values of Vref from 2 V to 7 V. The measured settling time of this DAC is 200 ns with C1 = 200 pF.
