Abel Raynus
EDN
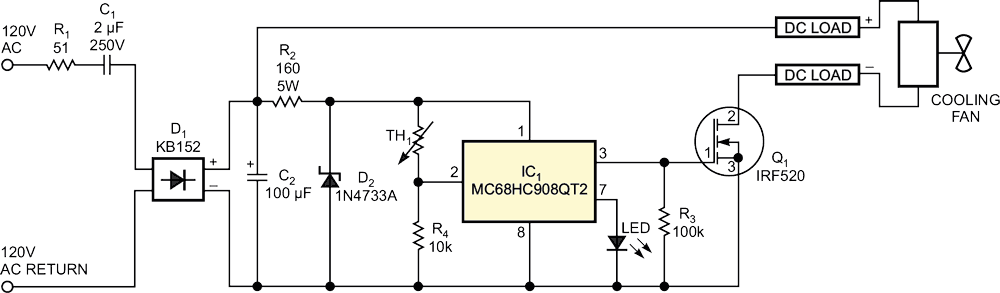
A microcontroller requires dc operating power in the 2 to 5.5 V range, an amount that a battery or a secondary power source can easily supply. However, in certain situations, a microcontroller-based product must operate directly from a 120 or 220 V-ac power outlet without a step-down transformer or a heat-producing, voltage-decreasing resistor. As an alternative, a polyester/polypropylene film capacitor rated for ac-line service can serve as a nondissipative reactance (Figure 1). Capacitor C1, a 2-µF AVX FFB16C0205K rated for 150 V rms, provides a significant ac-voltage drop that reduces the voltage you apply to a diode-bridge rectifier, D1.
 |
||
| Figure 1. | C1 provides capacitive reactance, which limits ac-input current without dissipating excessive heat in this dc fan-speed controller. |
|
A flameproof metal-film resistor, R1, limits current spikes and transient voltages induced in the ac-power line by lightning strikes and abrupt load changes. In this application, the ac current does not exceed 100 mA rms, and a 51 Ω, 1 W resistor provides adequate current limiting. R2, a 5 W, 160 Ω Yageo type-J resistor, and D2, a 1N4733A zener diode, provide 5 V regulated power for the microcontroller, a Freescale MC68HC908QT2.
 |
||
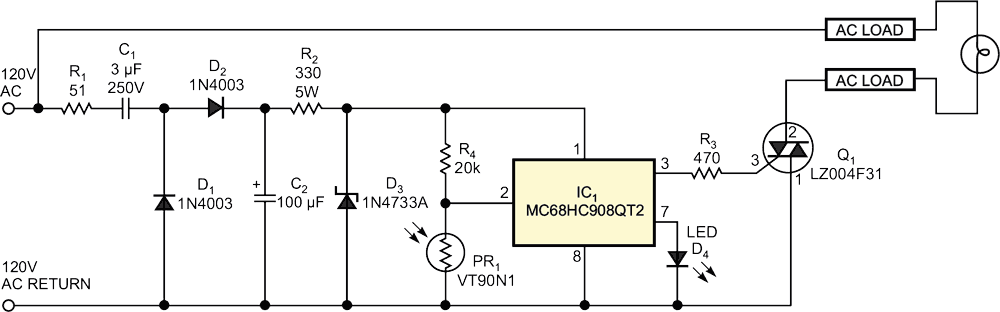
| Figure 2. | A two-diode rectifier and lamp-control bidirectional thyristor share a common return path to the ac line. |
|
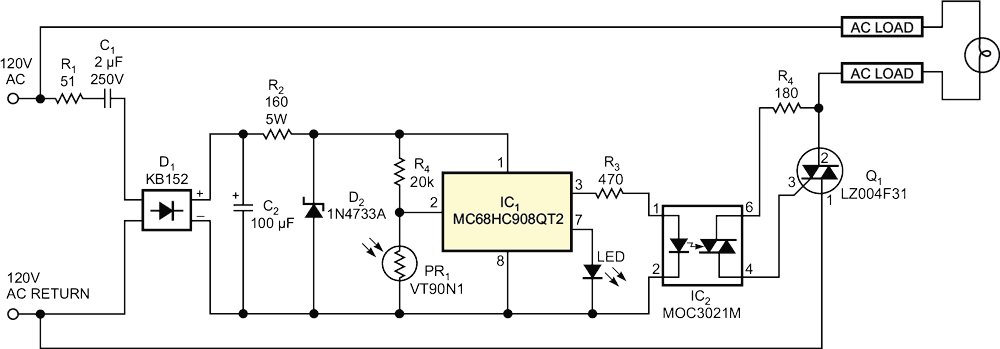
The schematic shows a representative circuit for a microcontroller-based fan-speed regulator in which a thermistor senses air temperature and the microcontroller drives a fan's motor. Figure 2 illustrates a light-intensity regulator based on an inexpensive two-diode rectifier and a bidirectional-thyristor-lamp controller that share a common ground. IC2, a Fairchild MOC3021M bidirectional-thyristor-driver optoisolator, separates the lamp-return path from the microcontroller's ground return (Figure 3). In each of the three circuits, the Kingbright W934GD5V0 LED indicator includes a built-in current-limiting resistor (not shown).
 |
||
| Figure 3. | An optoisolator separates the bidirectional thyristor’s high-current ac-line return path from the microcontroller’s power supply. |
|
