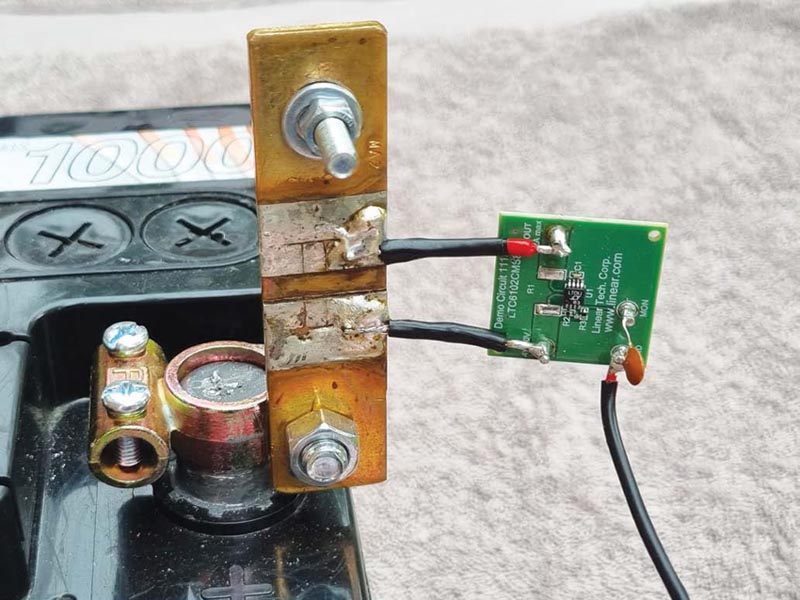
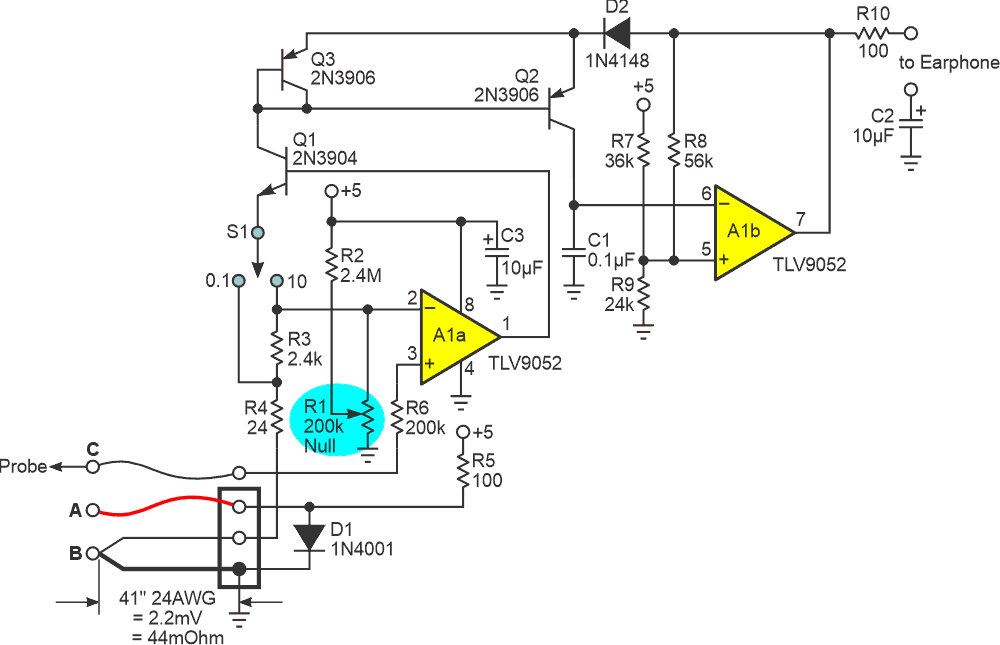
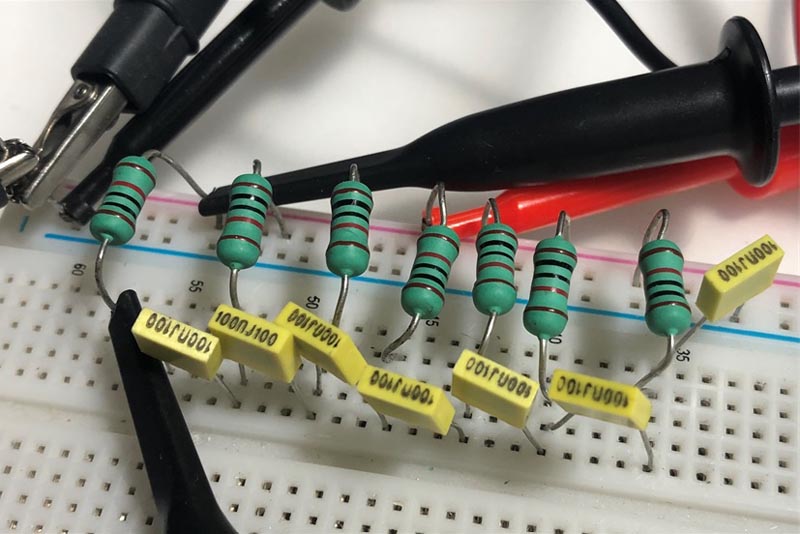
Recently, frequent and favorite contributor Nick Cornford gave us a cool and novel acoustic-interface design for a super sub-ohmmeter capable of audibly sniffing out defects in PWBs...
This article describes a circuit that facilitates the measurement of currents from amps to hundreds of amps with a high degree of precision. Introduction...
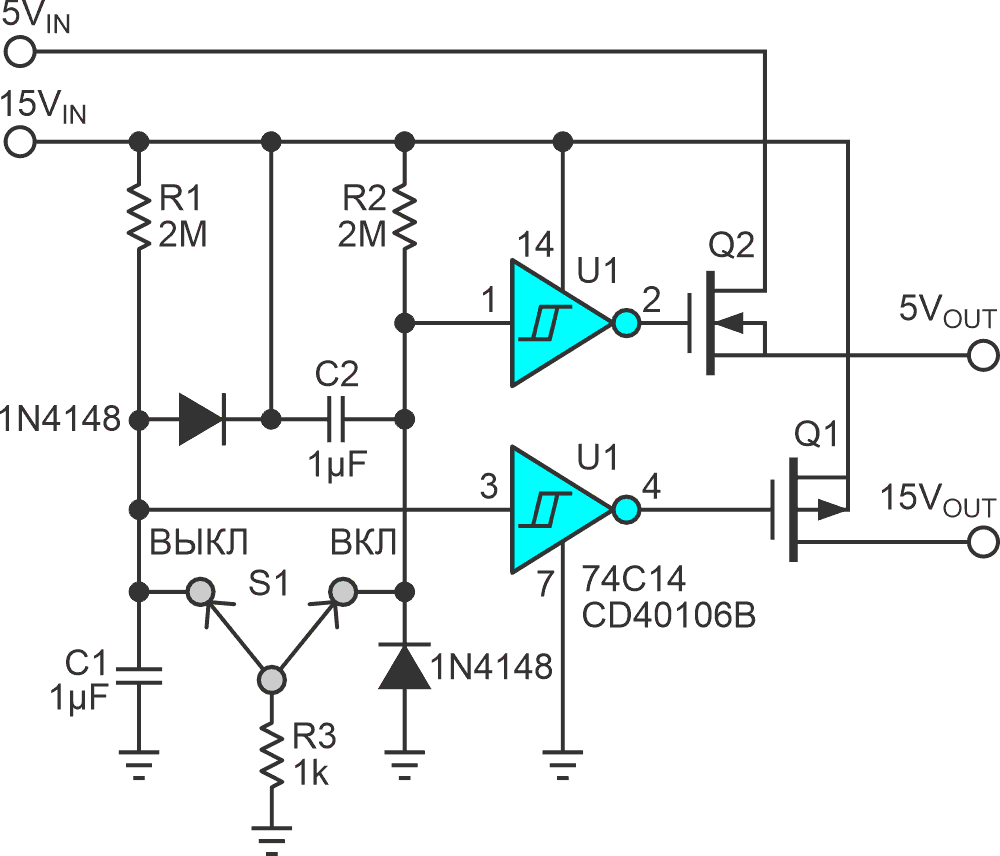
Frequent contributor R. Jayapal recently shared an interesting Design Idea for power supply control and sequencing in MCU-based applications that combine analog and digital circuitry...
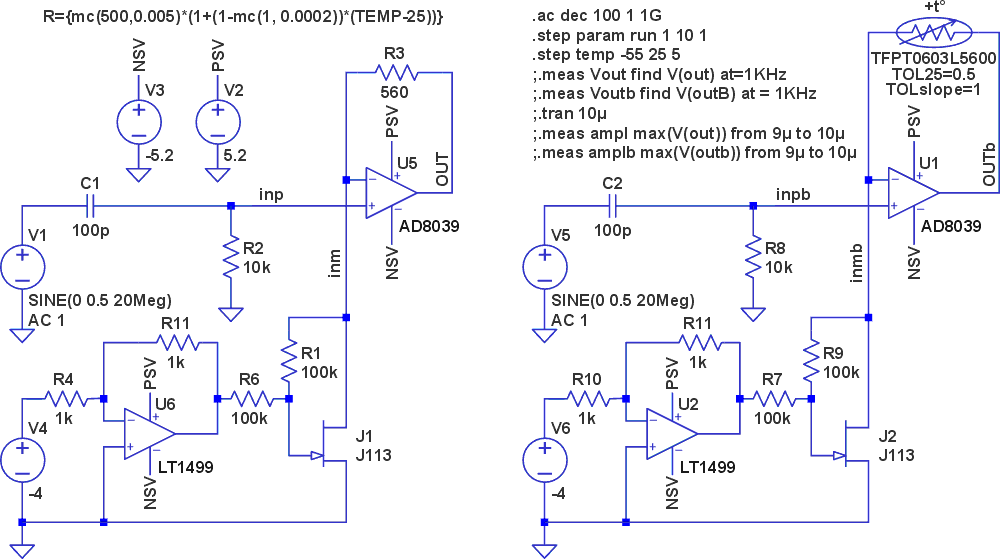
With the trend toward miniaturization, temperature effects in power electronics are more pronounced than ever. If you’re dealing with temperature fluctuations in your circuit, you may need a stabilization system to keep the temperature constant and minimize noise in the circuit response...
WIZnet is releasing ioPort, a new RJ45-style module series made to add Ethernet to embedded products with less PCB work and faster time-to-market...
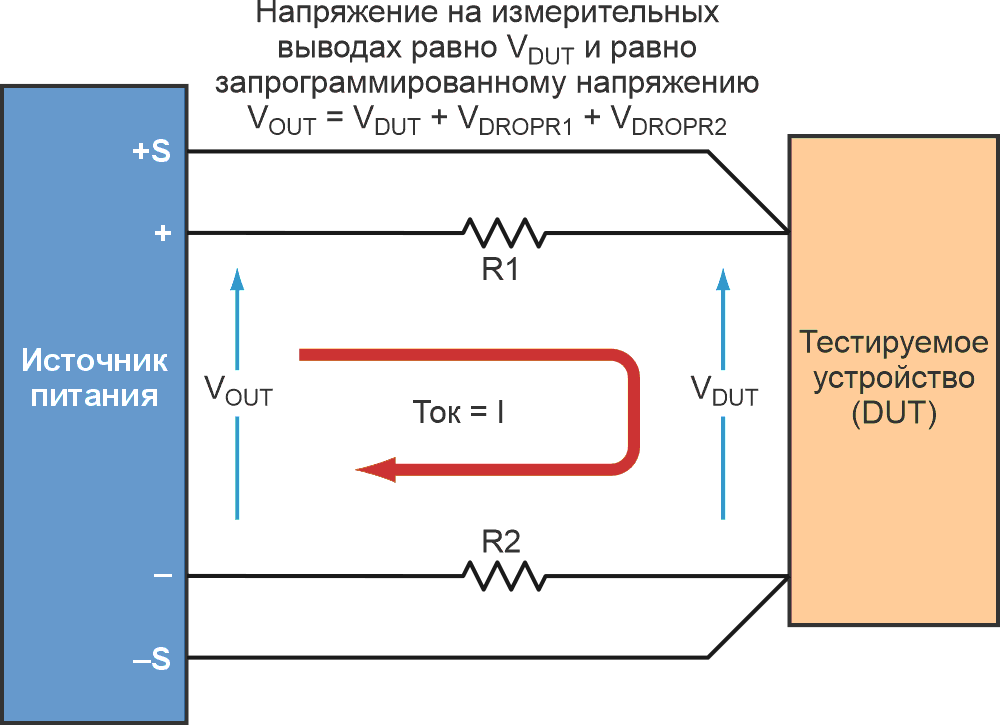
I’ve been working with dc power supplies and batteries for over 30 years now and every day I employ Ohm’s Law, V = I·R, to solve some problem or make some calculation related to dc power...
Could a simple passive RC network without any transformers, inductors, switches, or non-linear components produce a voltage gain?...
Toshiba Electronics expands its electronic fuse (eFuse) lineup with the introduction of the 40 V TCKE6 series...
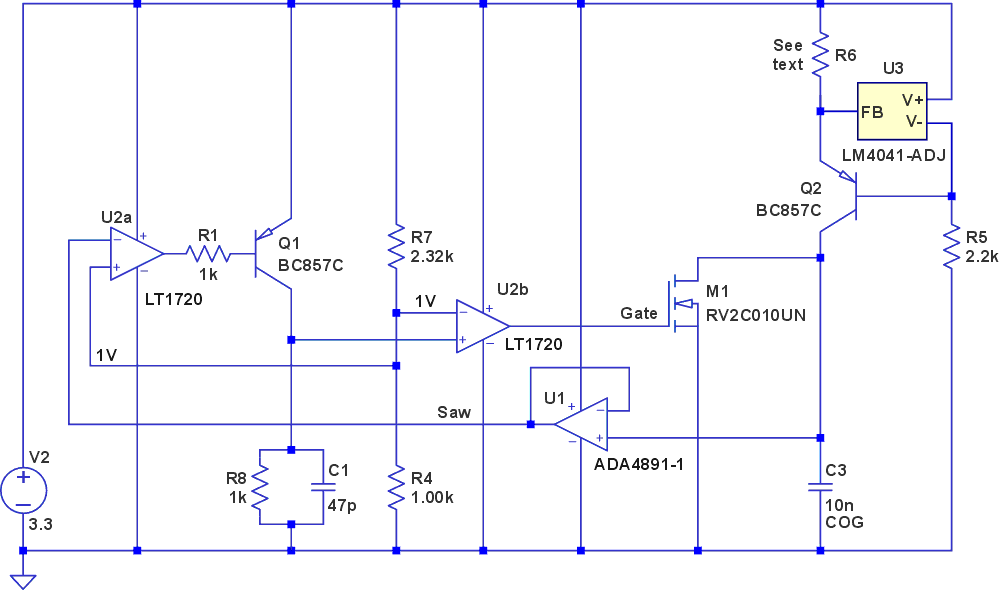
There are many ways of generating analog sawtooth waveforms with oscillating circuits. Here’s a method that employs a single supply voltage rail to produce a buffered signal whose frequency can be varied over a range from 10 Hz to 1 MHz...
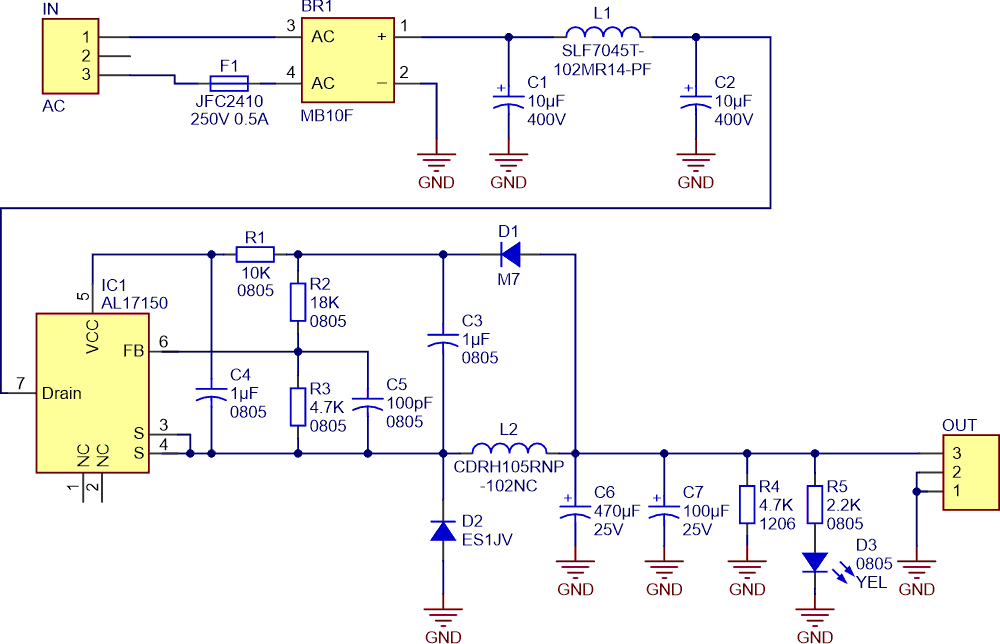
Whenever you hear the transformerless supply term, you initially imagine the capacitor-based solution: a high-voltage non-polarized capacitor in series with the mains line, a bridge rectifier, a Zener diode, and a filtering electrolytic capacitor...