White-noise generators generate a flat graph of output-power density versus frequency. These generators are useful for testing circuits that have an extended low-frequency or dc response. However, the presence of pink, or flicker, noise complicates the design of white-noise generators for frequency ranges that extend to a few hertz or below. A semiconductor device generates noise that always has the characteristic signature of pink noise: Its output-power-density amplitude increases as frequency decreases, with a corner frequency of 10s of hertz to a few kilohertz. A high-value resistor generates noise with its own flicker-noise component, whose value and characteristics vary with the resistor’s technology. If, on the other hand, the resistor has a low value and the device uses low-noise technology, then the noise is almost completely white with power density that is constant with frequency. Unfortunately, a low-value resistor also yields a low value of noise-power-density amplitude, and any device you introduce to amplify that level adds pink noise of its own.
You can find amplifiers whose input-voltage noise includes no pink-noise component, but their input-current noise has a flicker-noise component, which appears at the amplifier output if the resistance that any amplifier input encounters has a significant value.
 |
||
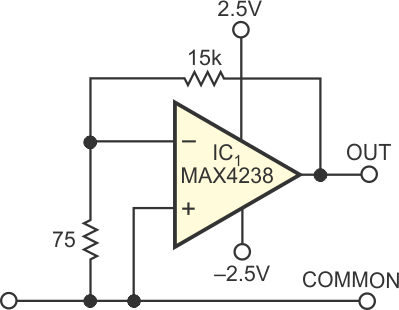
| Figure 1. | Built with an amplifier whose input voltage noise has no flicker-noise component, this white-noise generator produces an output with no flicker-noise component. |
|
In the noise-generator circuit of Figure 1, IC1, a MAX4238 amplifier from Maxim has no flicker-noise component in its input-voltage noise. It amplifies its own input-voltage noise with a feedback network comprising low-value resistors to avoid adding noticeable flicker-component noise from either the resistors or the amplifier’s input-noise current.
 |
||
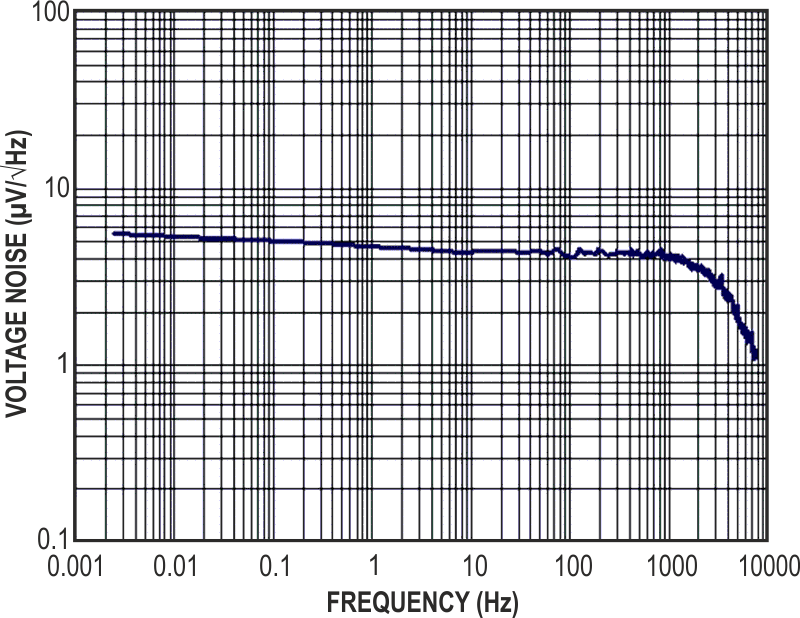
| Figure 2. | The circuit's output voltage as a function of frequency is almost flat from 0.01 Hz to 3 kHz. |
|
A plot of the circuit’s output voltage as a function of frequency is almost flat from 0.01 Hz to 3 kHz (Figure 2). The voltage-density amplitude is 4 to 5 µV/√Hz. The noise-density amplitude also depends on temperature, so you should keep the circuit at constant temperature while making measurements.