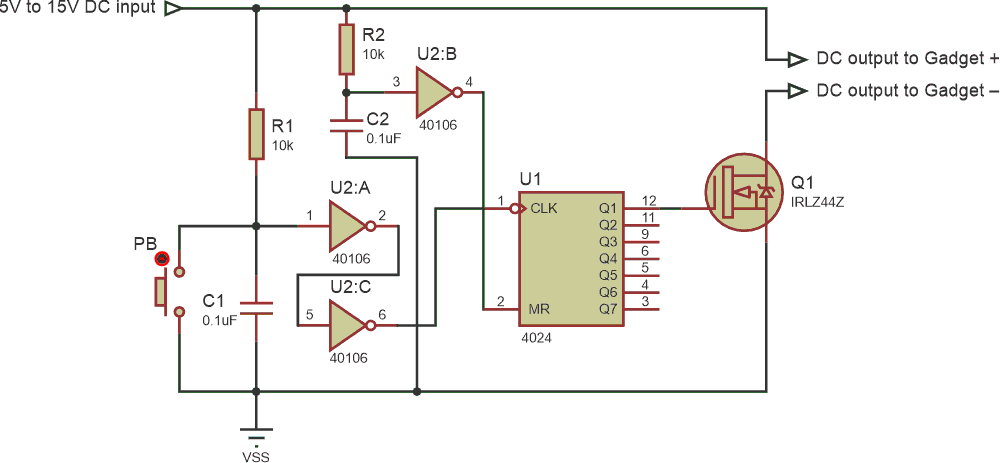
Figure 1 gives a simple circuit for the PUSH ON, PUSH OFF function with only a few inexpensive components. In this design, the output is connected to the input of the gadget when you press the push button (PB) once. For the next push, the output is disconnected.
 |
|
| Figure 1. | A Flip ON Flop OFF circuit for DC voltages. The gadget is connected to the output terminals of the PB. With an adequate heat sink for MOSFET Q1, the output current can go up to 50 A. |
This is an attractive alternative to bulkier ON/OFF switches for DC circuits. The circuit has a fairly simple explanation. U1 is a counter.
During power on, R2/C2 resets the counter to zero. When you push PB momentarily once, a pulse is generated and shaped by a Schmidt trigger inverter U2 (A & C), which counter U1 counts. Hence, the LSB (Q1) output of U1 becomes HIGH, making MOSFET Q1 conduct. At this point, the output gets the input DC voltage.
When you push PB momentarily again, another pulse is generated and counted by U1. Hence, its LSB (Q1) output goes LOW and MOSFET Q1 stops conducting and output is disconnected from input. This action continues, making output ON and OFF for each push of PB.